AWS Global Accelerator is a service that can improve availability and performance of your applications for local and global users.
It directs traffic to optimal endpoints over the AWS global network. This improves the availability and performance of your internet applications that are used by a global audience.
By default, it provides you with two static IP addresses that you associate with your accelerator. Alternatively you can bring your own IP Addresses.
How It Works
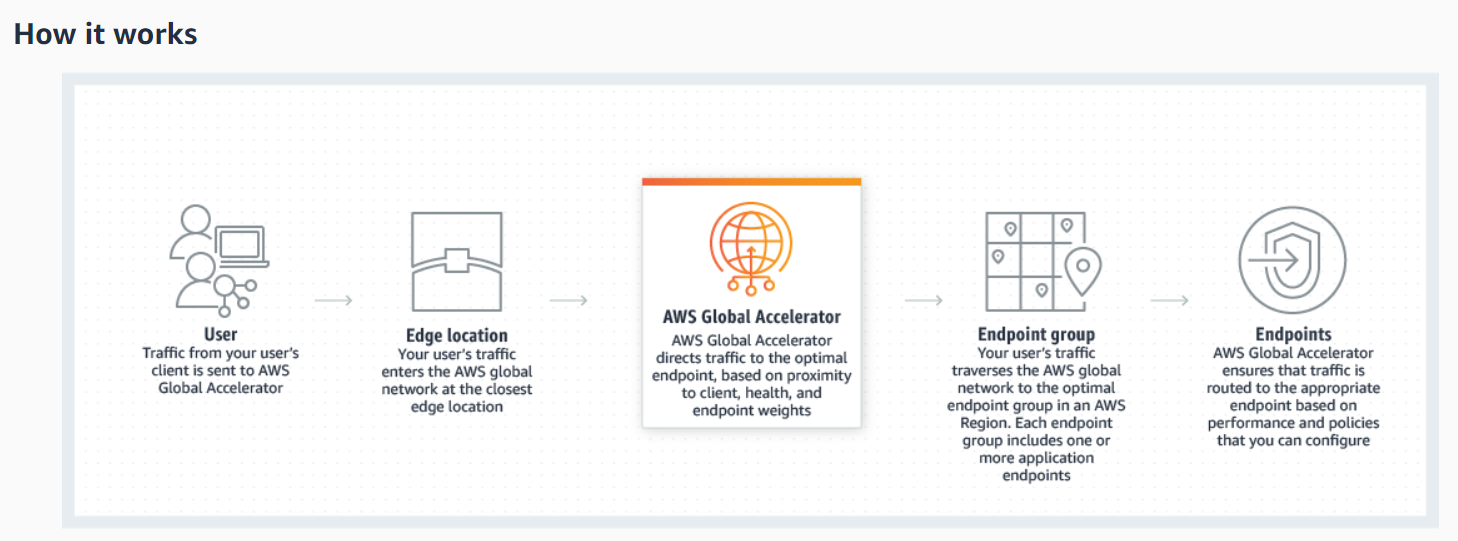
It includes the following components:
- Static IP addresses - 2 static IP Addresses
- Accelerator - each accelerator includes one or more listeners
- DNS Name - Global Accelerator assigns each accelerator a default DNS name (abc.awsglobalaccelerator.com)- that points to the static IP addresses that Global Accelerator assigns to you. Depending on the use case, you can use your accelerators static IP or DNS name to route traffic to your accelerator, or set up DNS records to route traffic using your own custom domain name.
- Network Zone - A network zone services the static IP addresses for your accelerator from a unique IP subnet. Similar to an AWS AZ, a network zone is an isolated unit with its own set of physical infrastructure. When you configure an accelerator, by default, Global Accelerator allocates two IPv4 addresses for it. If one IP address from a network zone becomes unavailable due to IP address blocking by certain client networks, or network disruptions, client applications can retry on the healthy static IP address from the other isolated network zone.
- Listener - A listener processes inbound connections from clients to Global Accelerator, based on the port (or port range) and protocol that you configure. Global accelerator supports both TCP and UDP protocols. Each listener has one or more endpoint groups associated with it, and traffic is forwarded to endpoints in one of the groups. You associate endpoint groups with listeners by specifying the Regions that you want to distribute traffic to. Traffic is distributed to optimal endpoints within the endpoint groups associated with the listener.
- Endpoint Group - Each endpoint group is associated with a specific AWS Region. Endpoint groups include one or more endpoints in the region. You can increase or reduce the % of traffic that would be otherwise directed to an endpoint group by adjusting a setting called a traffic dial. The traffic dial lets you easily do performance testing or blue/green deployment testing for new releases across different AWS Regions
- Endpoint - they can be Network load balancers, Application load balancers, ec2 instances, or elastic IPs. An application load balancers can be internet-facing or internal. Traffic is routed to endpoints based on configuration options that you choose, such as endpoint weights. For each endpoint, you can configure weights, which are numbers that you can use to specify the proportion of traffic to route to each one. This can be useful, for example, to do performance testing within a region.

