Operational Excellence
— Includes the ability to run and monitor systems to deliver business value and continually improve supporting processes and procedures
— Design Principles
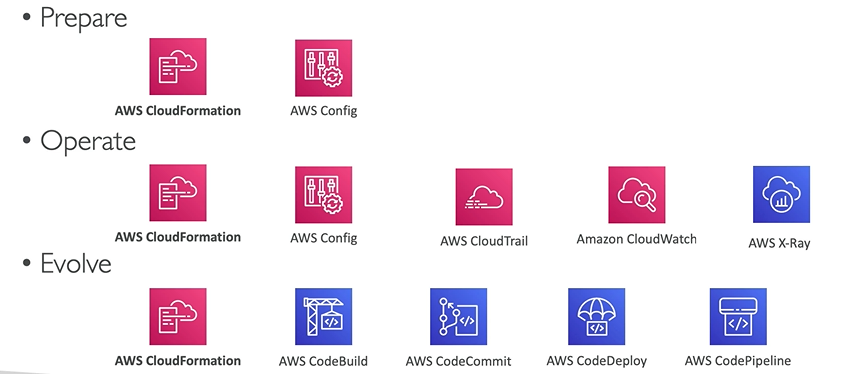
- Perform operations as code - Infrastructure as code
- Annotate documentation - Automate the creation of annotated documentation after every build
- Make frequent, small, reversible changes
- Refine operations procedure frequently - and ensure team members are familiar with it
- Anticipate failure
- Learn from all operational failures
Security
— Includes the ability to protect information, systems, and assets while delivering business value through risk assessments and mitigation strategies
— Design Principles
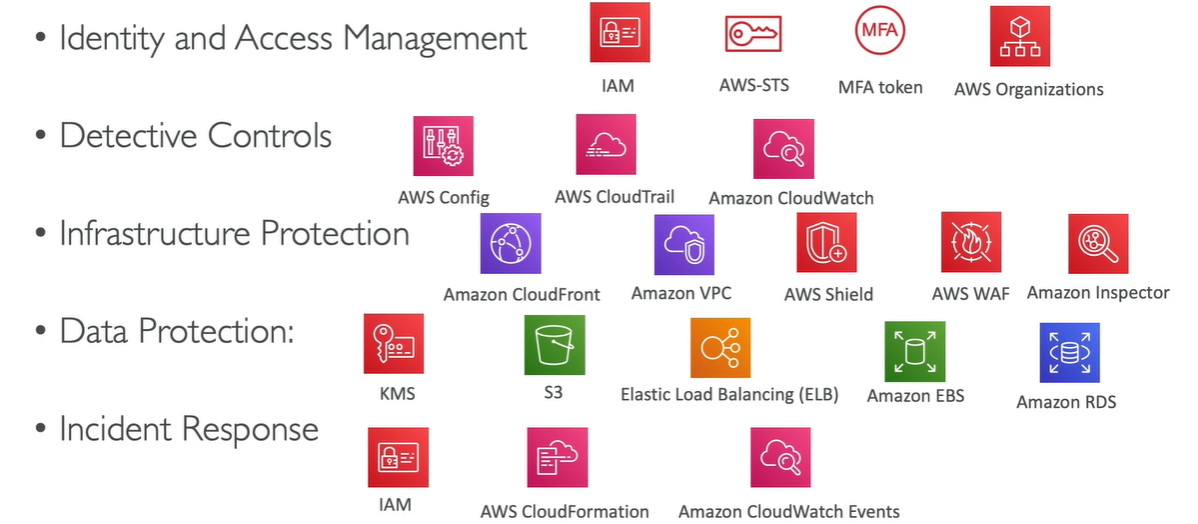
- Implement a strong identity foundation - Centralize privilege management and reduce (or even eliminate) reliance on long-term credentials - Principle of least privilege - IAM
- Enable traceability - Integrate logs and metrics with systems to automatically respond and take action
- Apply security at all layers - like edge network, VPC, subnet, load balancer, every instance, OS and application
- Automate security best practices
- Protect data in transit and at rest - Encryption, tokenization and access control
- Keep people away from data - Reduce or eliminate the need for direct access or manual processing of data
- Prepare for security events - Run incident response simulations and use tools with automation to increase your speed for detection, investigation and recovery
Reliability
— Ability of a system to recover from infrastructure or service disruptions, dynamically acquire computing resources to meet demand, and mitigate disruption such as misconfiguration or transient network issues
— Design Principles
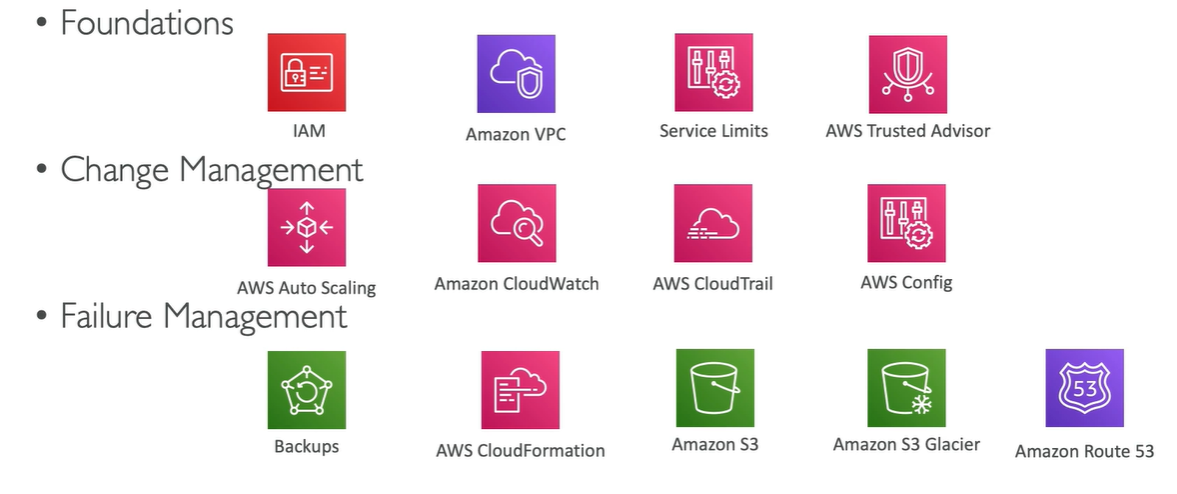
- Test recovery procedures - Use automation to simulate different failures or to recreate scenarios that led to failures before
- Automatically recover from failure - Anticipate and remediate failures before they occur
- Scale horizontally to increase aggregate system availability - Distribute requests across multiple, smaller resources to ensure that they don't share a common point of failure
- Stop guessing capacity - Maintain the optimal level to satisfy demand without over or under provisioning - use auto scaling
- Manage change in automation - Use automation to make changes to infrastructure
Performance Efficiency
— Includes the ability to use computing resources efficiently to meet system requirements, and to maintain that efficiency as demand changes and technology changes
— Design Principles
- Democratize advanced technologies - Advance technologies become services and hence you can focus more on product development
- Go global in minutes - Easy deployment in multiple regions
- Use Serverless architecture - avoid burden of managing servers
- Experiment more often - Easy to carry out comparative testing
- Mechanical sympathy - be aware of all AWS services

Cost Optimization
— Includes the ability to run systems to deliver business value at the lowest price point
— Design Principles
- Adopt a consumption mode - Pay only for what you use
- Measure overall efficiency - Use CloudWatch
- Stop spending money on data center operations - AWS does the infrastructure part and enables customer to focus on organization projects
- Analyze and attribute expenditure - Accurately identification of system usage and costs, helps measure return on investment (ROI) - make sure to use tags
- Use managed and application level service to reduce cost of ownership - As managed services operate at cloud scale, they offer cost per transaction or service